2009 ADA Code: A Comprehensive Guide for Accessibility Compliance
Understanding the 2009 ADA Code is crucial for any business or organization aiming to ensure accessibility for individuals with disabilities. This guide will delve into the intricacies of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 2009, providing you with a detailed overview of its provisions and how they affect your establishment.
What is the 2009 ADA Code?
The 2009 ADA Code, also known as the Americans with Disabilities Act Standards for Accessible Design, is a set of guidelines that outlines the minimum requirements for making buildings, facilities, and public spaces accessible to individuals with disabilities. These standards were established to ensure that people with disabilities have equal access to goods, services, facilities, privileges, advantages, or accommodations.
Scope of the 2009 ADA Code
The 2009 ADA Code applies to a wide range of entities, including businesses, non-profits, and government agencies. It covers various aspects of accessibility, such as physical access, communication, and employment. Let’s explore these dimensions in more detail.
Physical Access
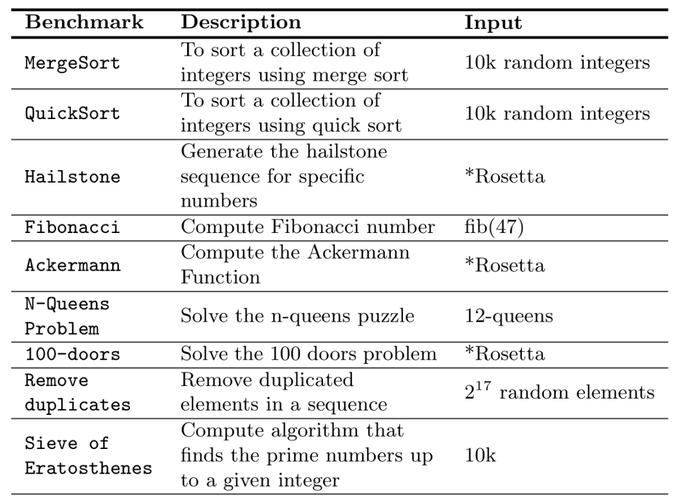
Physical access is a fundamental aspect of the 2009 ADA Code. It requires that buildings and facilities be designed and constructed to accommodate individuals with disabilities. Here are some key points to consider:
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Entrances and Exits | Accessible routes must be provided at each entrance and exit, including ramps, curb cuts, and automatic doors. |
| Restrooms | Accessible restrooms must be provided, with features such as grab bars, lever handles, and ample space for maneuvering wheelchairs. |
| Water Fountains | Accessible water fountains must be installed at a height that is reachable by individuals using wheelchairs. |
| Signage | Clear and visible signage must be provided to guide individuals with disabilities to accessible areas. |
Communication
Effective communication is essential for individuals with disabilities to fully access goods and services. The 2009 ADA Code addresses communication barriers by requiring entities to provide auxiliary aids and services, such as:
- Qualified interpreters for individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing
- Transcripts or captioning for audio and video materials
- Large-print materials for individuals with visual impairments
- Assistive listening devices
Employment
The 2009 ADA Code also covers employment practices, ensuring that individuals with disabilities have equal opportunities in the workplace. Key provisions include:
- Recruitment and hiring practices that do not discriminate against individuals with disabilities
- Reasonable accommodations for employees with disabilities, such as modified work schedules, assistive technology, and modified workspaces
- Training and awareness programs for employees on the rights and responsibilities under the ADA
Compliance and Enforcement
Ensuring compliance with the 2009 ADA Code is essential for any entity that falls under its purview. Compliance can be achieved through the following steps:
- Conducting a thorough assessment of your facility to identify potential barriers to accessibility
- Developing a plan to address these barriers and make necessary modifications
- Training staff on the requirements of the ADA and how to provide accessible services
- Regularly reviewing and updating your compliance efforts to ensure ongoing accessibility
Enforcement of the 2009 ADA Code is the responsibility of the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ). Entities that fail to comply with the ADA may face legal action, including fines and penalties.
Conclusion
The 2009 ADA Code is a vital tool for ensuring accessibility and inclusion for individuals with disabilities. By understanding and adhering to its provisions, you can create a more welcoming and accessible environment for all. Remember, compliance with the ADA not only benefits individuals with disabilities but also enhances your business’s reputation and bottom line.


