Understanding ADAS Sensor Recalibration: A Comprehensive Guide
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) have revolutionized the automotive industry, enhancing safety and convenience for drivers. At the heart of these systems are sensors that gather crucial data to assist with various functions like adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and parking assistance. However, these sensors can degrade over time or become misaligned, necessitating recalibration. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of ADAS sensor recalibration, exploring its importance, methods, and potential challenges.
Why is ADAS Sensor Recalibration Necessary?
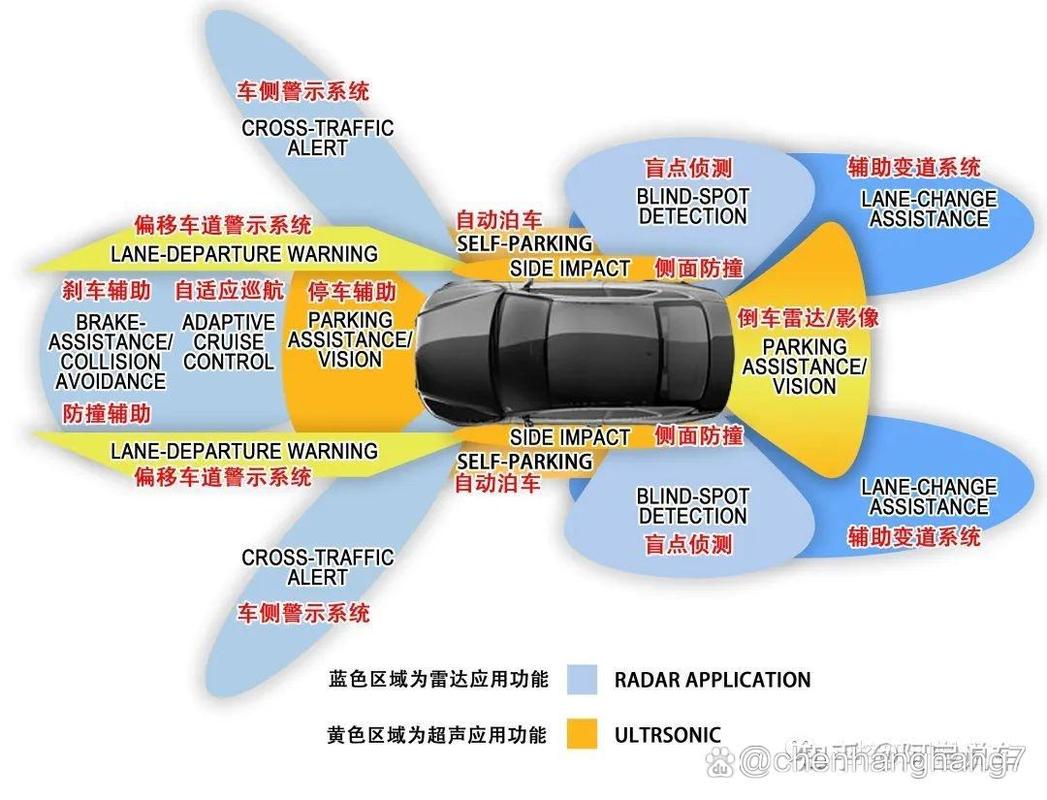
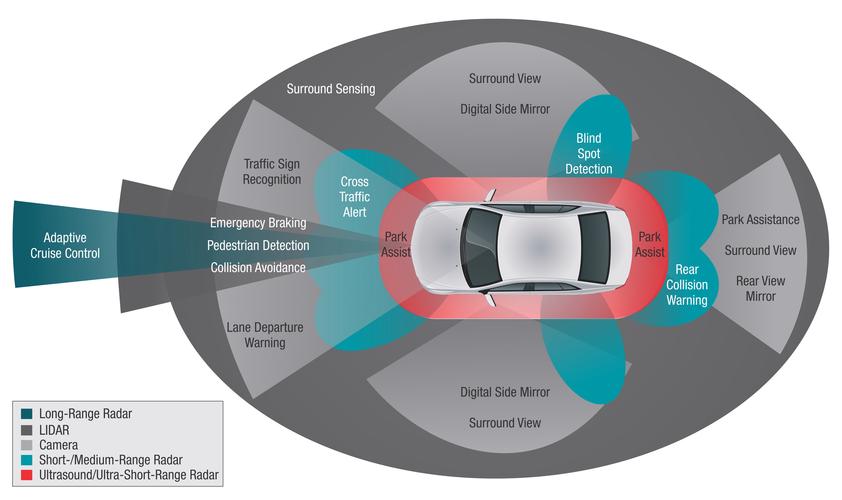
ADAS sensors, such as radar, LiDAR, and cameras, are designed to provide accurate data for the vehicle’s systems. However, several factors can lead to inaccuracies:
-
Environmental Conditions: Dust, dirt, and weather conditions can affect sensor performance.
-
Physical Damage: Accidents or impacts can cause sensors to misalign or become damaged.
-
Age and Wear: Over time, sensors can degrade, leading to reduced accuracy.
Recalibrating these sensors ensures that they continue to provide accurate data, maintaining the reliability and safety of the ADAS system.
Methods of ADAS Sensor Recalibration
There are several methods for recalibrating ADAS sensors, each with its own advantages and limitations:
1. On-Board Calibration
On-board calibration involves using the vehicle’s own systems to recalibrate the sensors. This method is typically used for sensors like cameras and radar. The process usually involves the following steps:
-
The vehicle is driven through a predefined path or course.
-
The sensors collect data during the drive.
-
The vehicle’s computer analyzes the data and adjusts the sensor settings accordingly.
This method is convenient and cost-effective, but it may not be suitable for all vehicles or sensor types.
2. Off-Board Calibration
Off-board calibration requires specialized equipment and is typically performed in a controlled environment. This method is more accurate and can be used for a wider range of sensors, including LiDAR. The process involves:
-
The vehicle is placed on a calibration rig or in a calibration bay.
-
The sensors are aligned and calibrated using the specialized equipment.
-
The vehicle’s computer is updated with the new sensor settings.
This method is more time-consuming and expensive but provides a higher level of accuracy.
3. Software Updates
In some cases, recalibration can be achieved through software updates. This method is typically used for sensors that can be updated remotely, such as cameras and radar. The process involves:
-
The vehicle’s computer receives the updated software.
-
The software is installed and the sensor settings are adjusted accordingly.
This method is convenient and cost-effective but may not be available for all vehicles or sensor types.
Challenges and Considerations
ADAS sensor recalibration can be a complex process, and several challenges and considerations should be taken into account:
-
Vehicle Compatibility: Not all vehicles are compatible with certain recalibration methods.
-
Expertise: Recalibration requires specialized knowledge and equipment.
-
Cost: The cost of recalibration can vary significantly depending on the method and vehicle type.
It is essential to consult with a qualified professional to ensure that the recalibration process is performed correctly and safely.
Conclusion
ADAS sensor recalibration is a crucial process that ensures the reliability and safety of modern vehicles. By understanding the importance, methods, and challenges of recalibration, drivers can make informed decisions and maintain their ADAS systems in optimal condition.
| Recalibration Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| On-Board Calibration | Convenient, cost-effective |



