Understanding ADAS Diagnostics: A Comprehensive Guide
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering drivers enhanced safety and convenience. However, to ensure these systems operate optimally, it’s crucial to understand ADAS diagnostics. This guide will delve into the intricacies of ADAS diagnostics, covering various aspects to help you navigate this complex topic.
What is ADAS Diagnostics?
ADAS diagnostics refers to the process of analyzing and interpreting data from the various sensors and cameras installed in modern vehicles. These diagnostics help identify any issues or malfunctions in the ADAS system, ensuring that it functions correctly and safely.
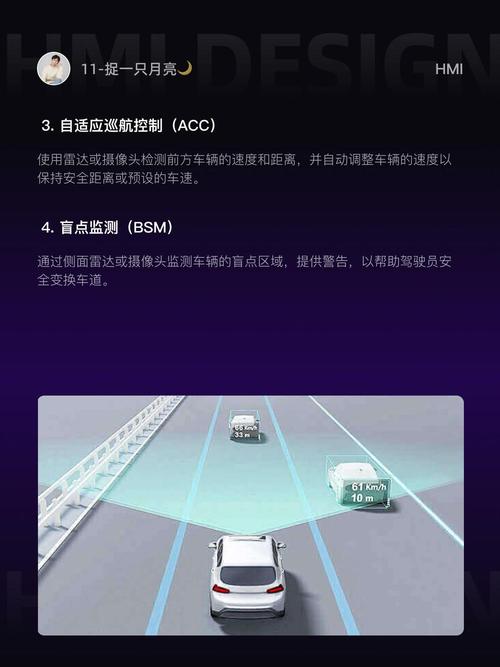
Key Components of ADAS Diagnostics
ADAS diagnostics involve several key components, each playing a vital role in the overall process:
-
Sensors: These devices, such as radar, LiDAR, and cameras, collect data about the vehicle’s surroundings.
-
Control Unit: The control unit processes the data from the sensors and makes decisions based on the vehicle’s environment.
-
Software: ADAS diagnostics software is used to analyze the data and identify any issues or malfunctions.

-
Diagnostic Tools: Specialized tools are used to connect to the vehicle’s onboard computer and retrieve diagnostic information.
Common ADAS Diagnostics Procedures
Several procedures are commonly used in ADAS diagnostics:
-
Visual Inspection: A visual inspection of the vehicle’s sensors and cameras can help identify any physical damage or debris that may affect their performance.
-
Calibration: Calibrating the sensors and cameras ensures they are aligned and functioning correctly.
-
Data Logging: Collecting and analyzing data from the sensors and cameras can help identify patterns or anomalies that may indicate a problem.
-
Software Updates: Updating the ADAS software can resolve issues or improve system performance.
Understanding Diagnostic Codes
Diagnostic codes are numerical codes that indicate specific issues within the ADAS system. These codes can be retrieved using a diagnostic tool and help technicians identify the root cause of the problem. Here are some common diagnostic codes and their meanings:
| Diagnostic Code | Description |
|---|---|
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient |
| P0440 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Flow Insufficient |
| P0600 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected |
| P0601 | Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit Malfunction |
Benefits of ADAS Diagnostics
ADAS diagnostics offer several benefits, including:
-
Enhanced Safety: Identifying and resolving issues in the ADAS system can help prevent accidents and ensure the safety of the vehicle’s occupants.
-
Improved Performance: Regular diagnostics can help maintain the optimal performance of the ADAS system, ensuring it operates as intended.
-
Cost Savings: Detecting and addressing issues early can help prevent more extensive and costly repairs in the future.
Conclusion
ADAS diagnostics is a crucial aspect of maintaining the functionality and safety of modern vehicles. By understanding the key components, procedures, and benefits of ADAS diagnostics, you can ensure that your vehicle’s ADAS system operates optimally and safely.



