Understanding the ADAS Calibration Process
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) have revolutionized the automotive industry, enhancing safety and convenience for drivers. One crucial aspect of ensuring the optimal performance of ADAS is the calibration process. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the ADAS calibration process, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of its various dimensions.
What is ADAS Calibration?
ADAS calibration is the process of adjusting and fine-tuning the sensors and cameras in an ADAS system to ensure they accurately detect and interpret the surrounding environment. This process is essential for the system to function correctly and provide the intended safety features.
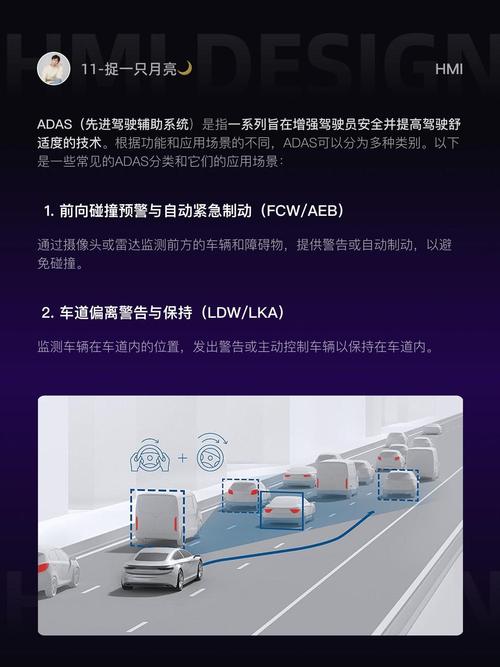
The Importance of Calibration
Calibration is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that the ADAS system operates within its designed specifications, providing reliable performance. Secondly, it helps in reducing false positives and negatives, which can lead to unnecessary stress or missed warnings. Lastly, calibration ensures that the system adapts to changes in the vehicle’s environment, such as changes in weather conditions or road surfaces.
Types of ADAS Calibration
There are several types of ADAS calibration, each catering to different aspects of the system. Here are some of the most common types:
-
Camera Calibration: This involves adjusting the camera’s focus, exposure, and white balance to ensure accurate image processing.
-
Millimeter Wave Radar Calibration: This type of calibration adjusts the radar’s beam pattern and sensitivity to ensure accurate detection of objects at varying distances.
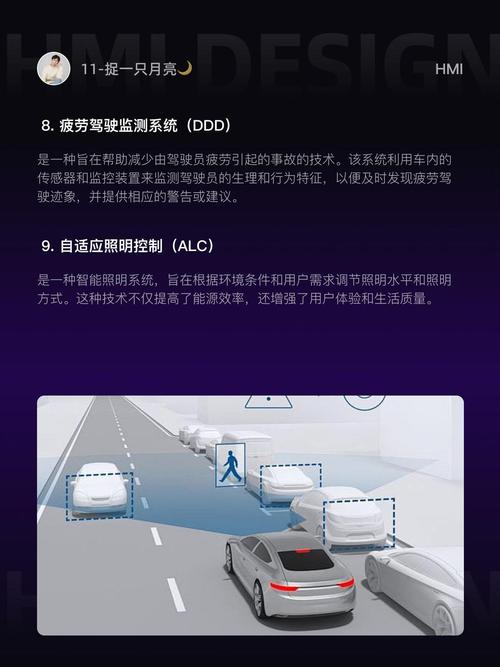
-
Lidar Calibration: Lidar calibration involves adjusting the laser’s emission and detection patterns to ensure accurate distance measurements.
-
Ultrasound Calibration: This type of calibration adjusts the ultrasound sensors to ensure accurate detection of objects in close proximity to the vehicle.
The Calibration Process
The ADAS calibration process typically involves the following steps:
-
Vehicle Preparation: The vehicle is prepared for calibration by ensuring that all necessary equipment is installed and functioning correctly.
-
Calibration Setup: The calibration equipment is set up in a controlled environment, such as a parking lot or a calibration tunnel.
-
Calibration Procedure: The calibration procedure involves driving the vehicle through the calibration environment while the equipment collects data from the sensors and cameras.
-
Data Analysis: The collected data is analyzed to identify any discrepancies or errors in the sensor readings.
-
Adjustments: Based on the data analysis, adjustments are made to the sensors and cameras to correct any errors.
-
Verification: The adjusted system is verified to ensure that it meets the required specifications.
Challenges in ADAS Calibration
ADAS calibration can be challenging due to several factors:
-
Environmental Conditions: Weather conditions, such as rain, snow, or fog, can affect the accuracy of the sensors and cameras.
-
Vehicle Variability: Different vehicles may have varying sensor placements and configurations, making it challenging to create a one-size-fits-all calibration process.
-
Complexity: The calibration process involves multiple sensors and cameras, each with its own calibration requirements.
Conclusion
ADAS calibration is a critical process that ensures the optimal performance of advanced driver-assistance systems. By understanding the various dimensions of the calibration process, you can appreciate the importance of this process and its impact on vehicle safety and convenience.



