2023 ADA Guidelines for Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the latest guidelines for managing diabetes is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals living with the condition. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) regularly updates its guidelines to reflect the latest research and advancements in diabetes care. In this detailed overview, we delve into the 2023 ADA guidelines for diabetes, covering various aspects of management, treatment, and prevention.
Management of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. The 2023 ADA guidelines emphasize the importance of intensive insulin therapy for achieving tight glycemic control. This includes multiple daily injections or an insulin pump, along with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to closely monitor blood sugar levels.
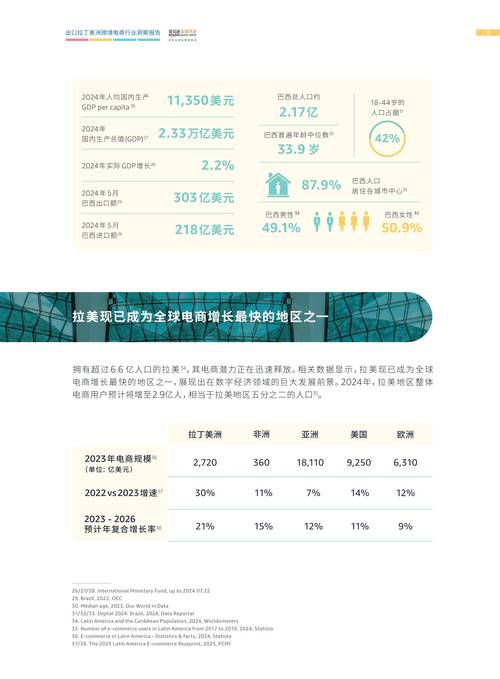
Table 1: Key Recommendations for Type 1 Diabetes Management
| Recommendation | Description |
|---|---|
| Intensive insulin therapy | Multiple daily injections or an insulin pump, along with CGM, to achieve tight glycemic control. |
| Education and support | Regular education on diabetes management, including insulin administration, blood sugar monitoring, and carbohydrate counting. |
| Monitoring for hypoglycemia | Regular monitoring for low blood sugar levels and immediate action to prevent severe hypoglycemia. |
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. The 2023 ADA guidelines highlight the importance of lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, as the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes. Medications, including metformin, may be added to manage blood sugar levels when lifestyle changes alone are insufficient.
Table 2: Key Recommendations for Type 2 Diabetes Management
| Recommendation | Description |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle modifications | Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. |
| Medications | Adding metformin or other medications, such as sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, or GLP-1 receptor agonists, as needed to achieve blood sugar targets. |
| Monitoring and follow-up | Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and follow-up with a healthcare provider to assess treatment effectiveness and make adjustments as necessary. |
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
The 2023 ADA guidelines emphasize the importance of preventing type 2 diabetes through lifestyle modifications. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet. The guidelines also recommend screening for prediabetes and implementing interventions for individuals at high risk of developing the condition.
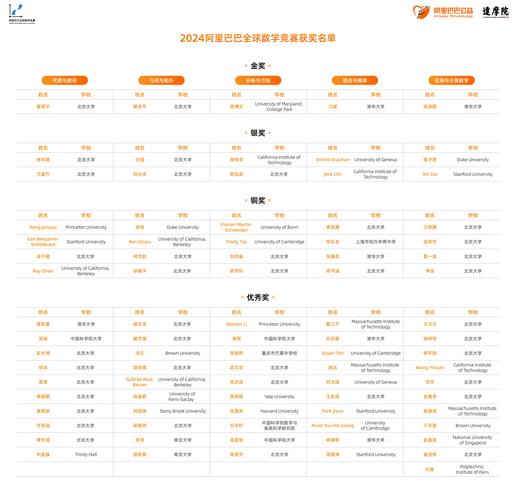
Table 3: Key Recommendations for Type 2 Diabetes Prevention
| Recommendation | Description |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle modifications | Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet. |
| Screening for prediabetes | Screening individuals at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such as those with a family history, obesity, or metabolic syndrome. |
| Interventions for high-risk individuals | Implementing lifestyle interventions or medications, such as metformin, for individuals at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. |
Management of Complications
Diabetes can lead to various complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems. The 2023 ADA guidelines emphasize the importance of managing these complications through regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications


