Understanding ADA and GPA: A Comprehensive Guide
What is ADA?
ADA, or Adenosine Deaminase, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of adenine nucleotides, which are essential components of DNA and RNA. This enzyme is found in various tissues and organs throughout the body, with particularly high activity in the thymus, spleen, and lymphoid tissues.
ADA is primarily responsible for converting adenine to inosine, a process that is vital for the recycling of adenine nucleotides. This recycling process is essential for maintaining cellular energy and preventing the accumulation of toxic metabolites.
ADA Testing Methods
Over the years, several methods have been developed to measure ADA activity. Here’s a brief overview of the evolution of ADA testing methods:
| Generation | Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Generation | PADA | Simple and easy to perform | Low sensitivity, not suitable for clinical applications |
| Second Generation | Berthelot’s reaction | Relatively simple and cost-effective | Low sensitivity, prone to interference |
| Third Generation | ADA coupled with glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH) | Improved sensitivity | Interference from serum ammonia, non-specific oxidation |
| Fourth Generation | ADA coupled with purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) and xanthine oxidase (XOD) | High sensitivity, accurate results | Complex and expensive |
Normal ADA Levels
Normal ADA levels in the blood vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test method used. However, a general range is as follows:
| Test Method | Normal ADA Levels (U/L) |
|---|---|
| Colorimetric method | 2-17 |
| Fluorescence polarization method | 2-17 |
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) | 2-17 |
ADA and Health Conditions
Abnormal ADA levels can indicate various health conditions. Here are some examples:
-
Increased ADA levels: Acute and chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, jaundice, malignancies, rheumatoid arthritis, typhoid fever, heart failure, and tuberculosis.
-
Decreased ADA levels: Hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, and certain types of lymphoma.
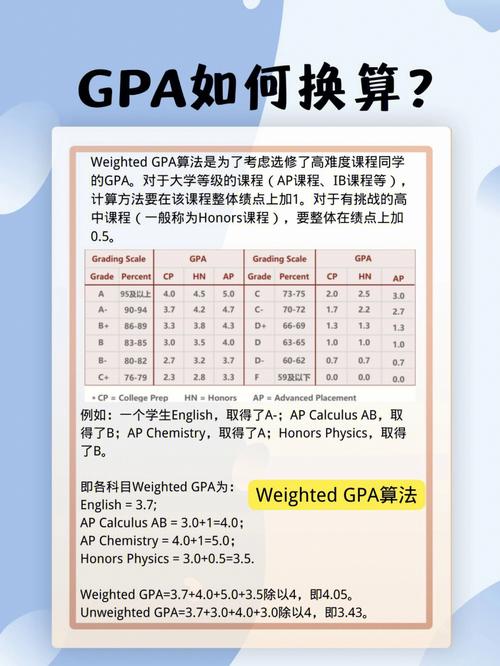
What is GPA?
GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a measure of academic performance that is commonly used in educational institutions worldwide. It represents the average of a student’s grades across various courses.
Calculating GPA
GPA is calculated by converting grades to points and then averaging those points across all courses. The specific method for calculating GPA can vary depending on the institution, but here’s a general approach:
-
Convert grades to points: Most institutions use a 4.0 scale, where A is 4.0, B is 3.0, C is 2.0, D is 1.0, and F is 0.0.
-
Calculate the total points: Multiply each grade point by the number of credits for the corresponding course.
-
Divide the total points by the total number of credits: This will give you the GPA.


